Instrumental and mathematical methods to assess the economic impact of COVID-19
Research relevance
Objec:
assessment of the economic impact of COVID-19Subject:
methods to assess the economic impact of COVID-19Objective:
research of methods to assess the economic impact of COVID-19Research objectives
Literature review
- Search of relevant literature
- Assessment of the relevance of the found literature using the method of linear convolution and selection
- Review of the selected literature sources
Assessment of the economic impact of COVID-19
- Selection of methods and problem formulation
- Data collection
- Modelling
- Data collection
Estimation of the relevance of the literature sources
\begin{aligned} y_{k} = \sum_{i\, =\, 1}^{m} u_{i} f_{i}(x_{k}),\\ \end{aligned} \begin{align*} & where\\ & x_{k} - an\:alternative, \\ & k - number\:of\:an\:alternative, \\ &m - number\:of\:criteria,\:required\:for\:assessment,\\ & f_{i} - function\:of\:assessment\:of\:an\:alternative\:x_{k}\:based\:upon\:criterion\:i,\\ & u_{i} - weight\:of\:the\:i-th\:criterion\:that\:has\:value\\ &between\:0\:and\:1.\\ \end{align*}
Selected scientific publications
- Multilayer artificial neural network for GDP prediction
- Probability-based approach to assess economic effects of COVID-19
- OLS-based method for assessing impact of non-pharmaceutical interventions
- Compartmental PEP Model for selecting optimal COVID-19 mitigation policies
- COVID-19 illness cost analysis in China
- Aggregate excess method for assessing the economic impact of COVID-19 on the retail sector of the United Kingdom
Selected scientific publications
- OLS-based method for assessing impact of non-pharmaceutical interventions
- COVID-19 illness cost analysis in China
- Aggregate excess method for assessing the economic impact of COVID-19 on the retail sector of the United Kingdom
Pandemic Economic Policy Model
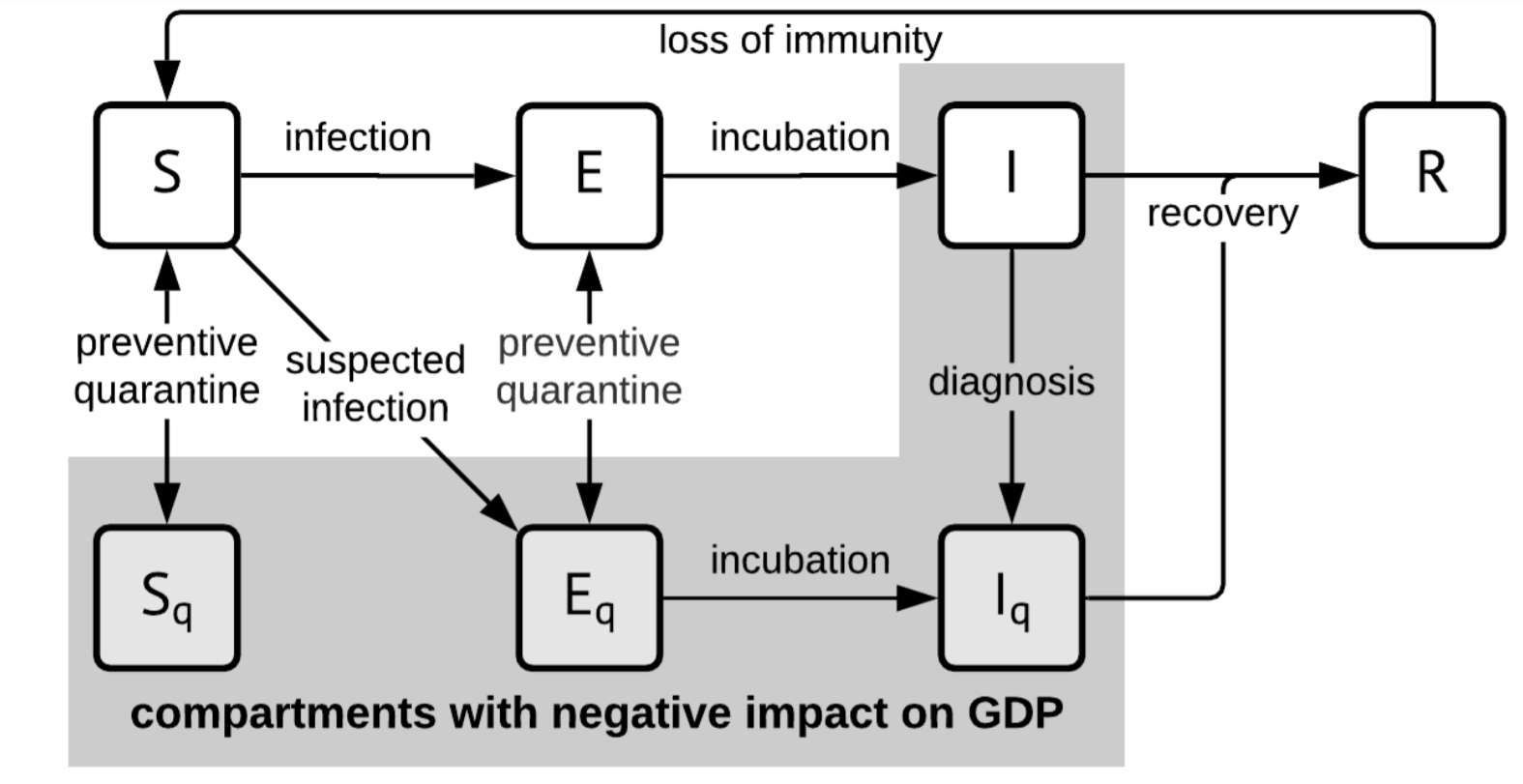
Economic extension of the PEP model
\begin{aligned} GDP' = b_{g} - p_{i}\,(\,p_{q\,i}\,S_{q}\:+\:e_{q\,i}\,E_{q}\:+\:i_{i}\,I\:+\:i_{q\,i}\,I_{q}\,),\\ \end{aligned} \begin{align*} & where\\ & b_{g} - GDP\:growth\:indicator\:at\:the\:beginning\:of\:pandemic,\\ & p_{i} - coefficients\:of\:the\:pandemic\:impact\:on\:GDP,\\ &S_{q},\,E_{q},\,I,\,I_{q} - share\:of\:quarantined\:individuals,\:\\ &at\:any\:stage\:of\:virus\:development,\:\, as\:well\:as\:share\:of\:the\:infected,\\ & p_{q\,i},\,e_{q\,i},\,i_{i},\,i_{q\,i} - coefficients\:which\:define\:the\:impact\:of\:the\:quarantined\:and\:infected\\ \end{align*}
Bezier Curves for NPI
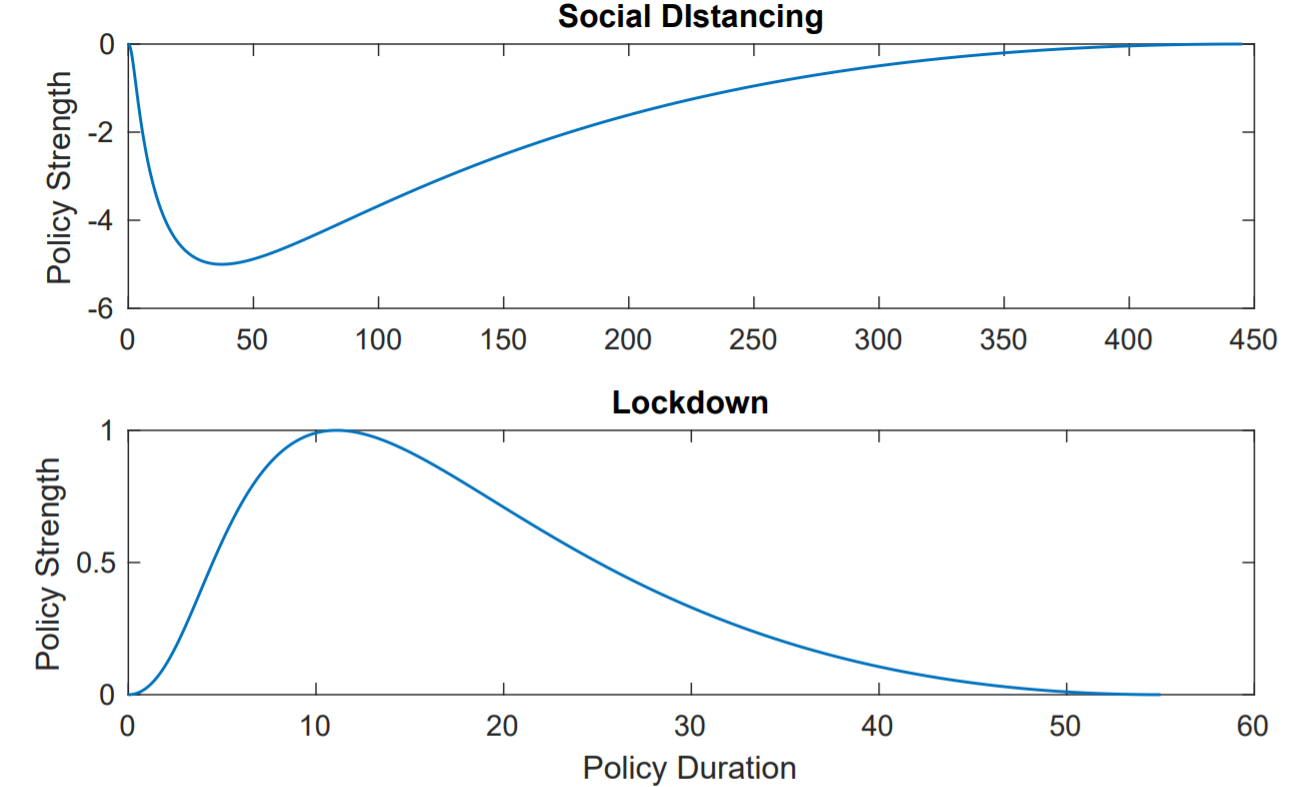
Search of the optimal time to take measures
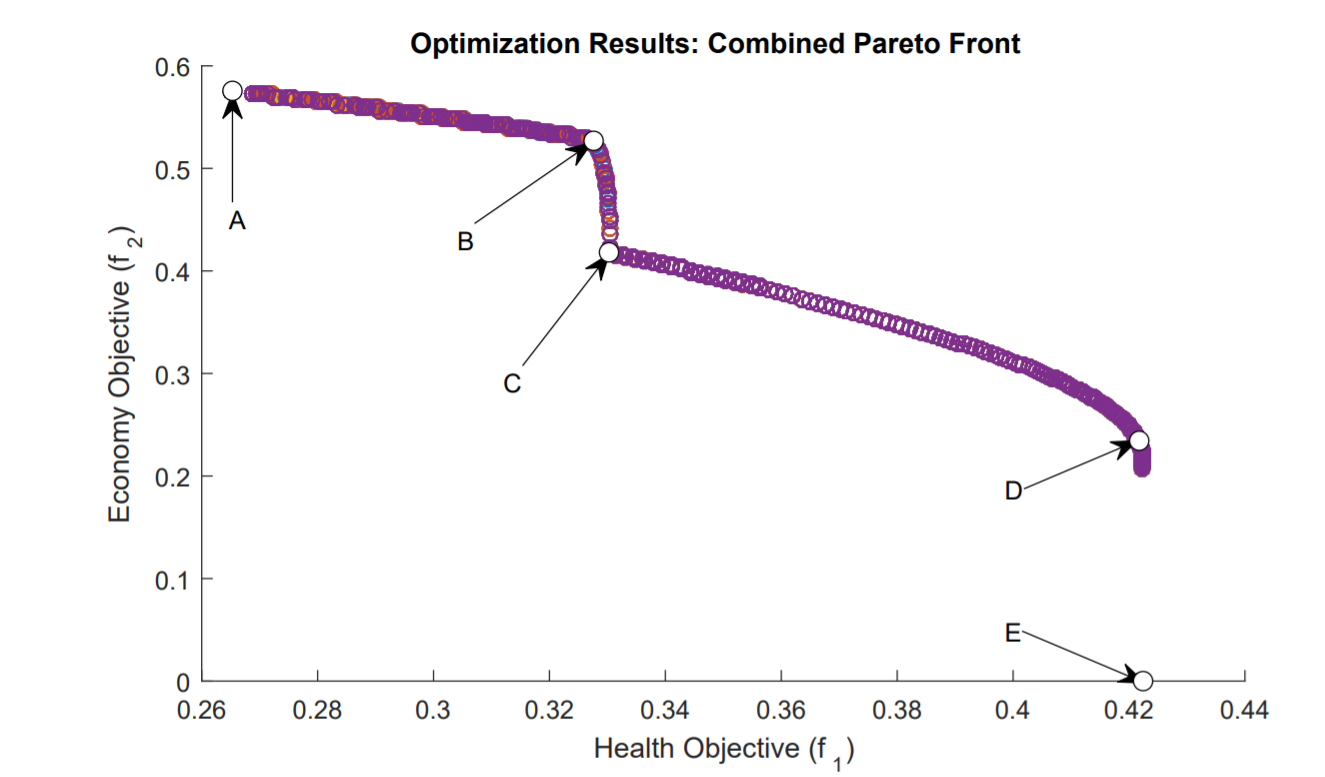
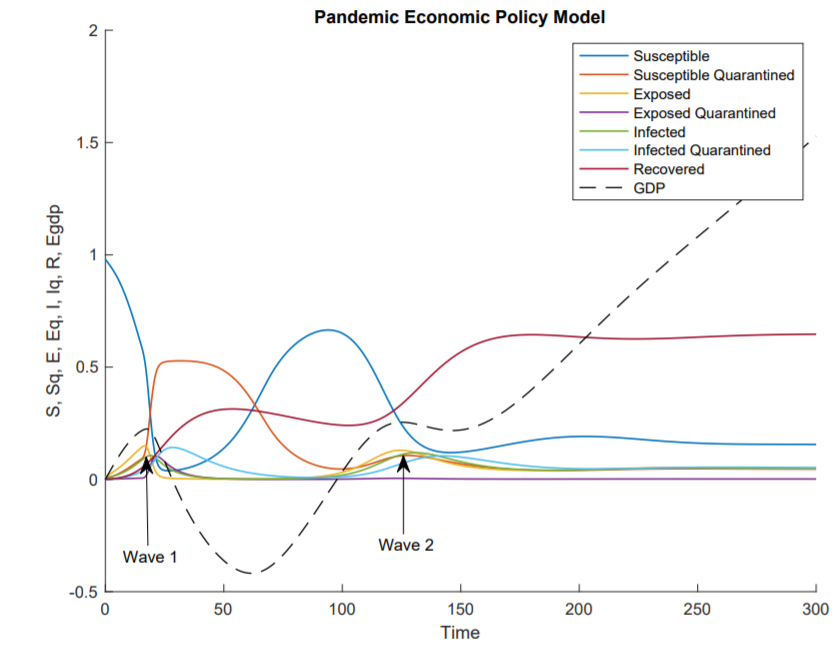
Cost of Illness Analysis
Direct medical costs
\begin{aligned} C = \sum_{x}\,p_{x}\,i_{x}\\ \end{aligned} \begin{align*} & where\\ & p_{x} - price\:of\:a\:medical\:component\\ &given\:its\:usage\:likelihood,\\ &i_{x} - number\:the\:patiens\:who\:need\:a\:component,\\ &x - type\:of\:a\:component\\ \end{align*}
Direct non-medical costs
\begin{aligned} TQC = \sum_{r}\sum_{e}\,75\,w_{r}\,d_{e}\,n_{e},\\ \end{aligned} \begin{align*} & where\\ & e - cause\:of\:quarantine,\\ &r - region's\:number,\\ &n_{e} - number\:of\:the\:quarantined\:individuals,\\ &d_{e} - duration\:of\:the\:quarantine\:depending\:on\:its\:causes \end{align*}
Labour productivity losses
\begin{aligned} CP_{r} = i_{r}\,f_{r}\,h_{r}\,q_{r},\\ \end{aligned} \begin{align*} & \\ & i_{r} - average\:daily\:salary,\\ &f_{r} - employment\:rate,\\ &h_{r} - average\:number\:of days\:lost\:due\:to\:imposed\:lockdown,\\ &q_{r} - population\:size, \end{align*}
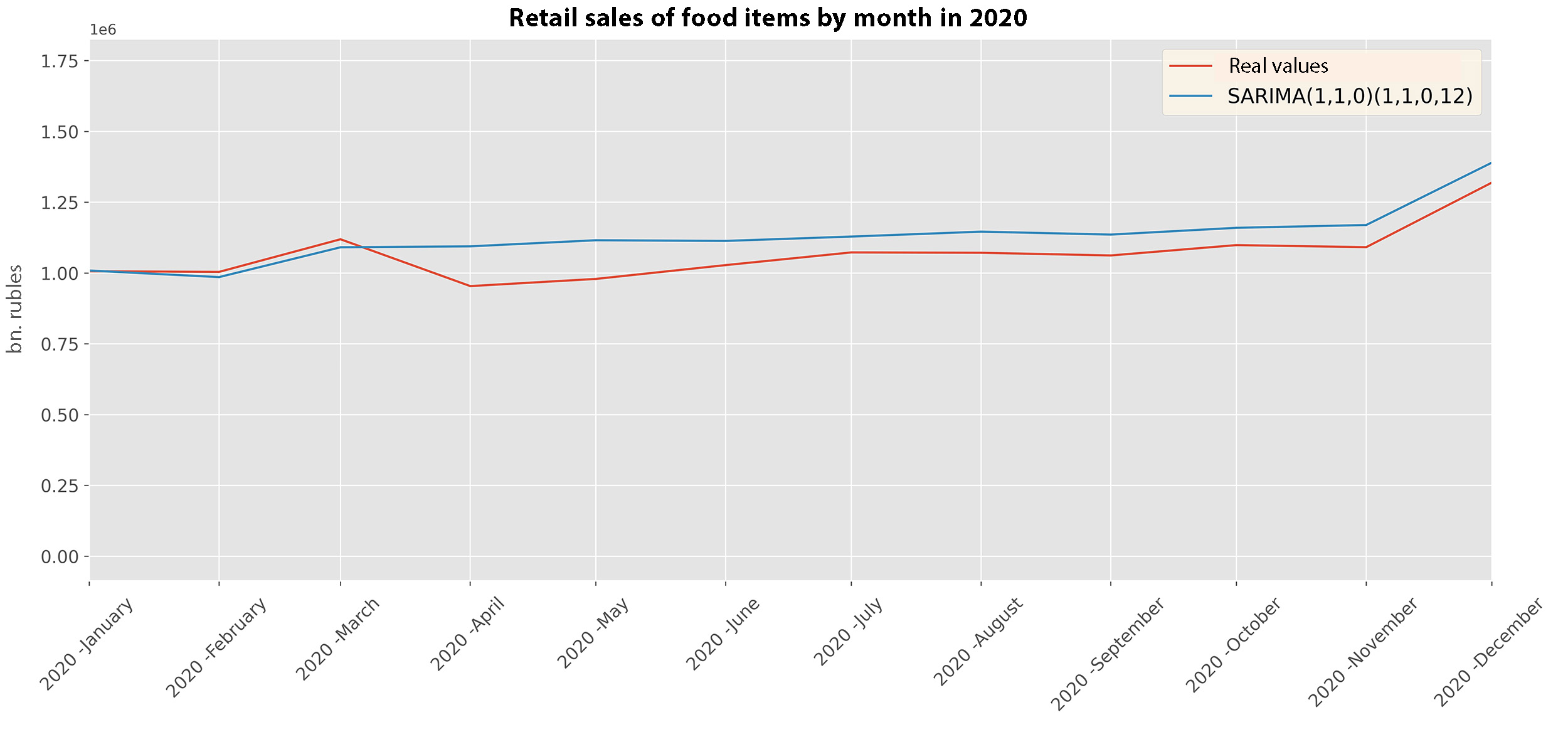
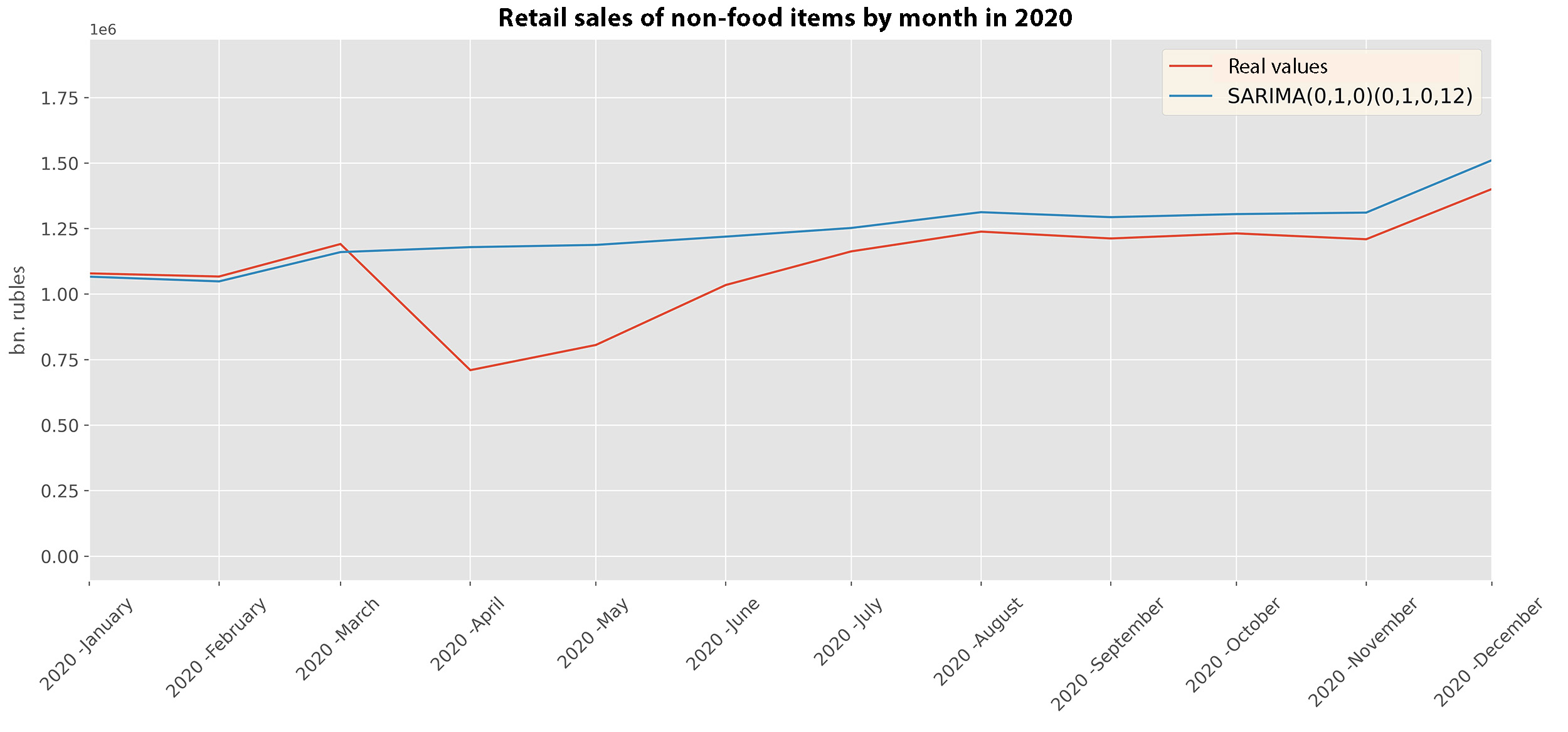
Aggregate excess method
\begin{aligned} S_{t}\,(\,C\,=\,1\,)\,-\,S_{t}\,(\,C\,=\,0),\\ \end{aligned} \begin{align*} & where\\ &S_{t} - sales\:volume\:at\:t\:point,\\ &C - indicator\:of\:the\:impact\:of\:COVID−19.\\ \end{align*}
Assessment of economic impact of COVID-19 on the Russian economy
Assessment levels
- Economy-wide
- Sector
- Subsector
Formula of lockdown costs calculation
\begin{aligned} Adjusted\:CP_{r} = i_{r}\,f_{r}\,h_{r}\,q_{r}\,(\,1\,-\,l_{r}\,),\\ \end{aligned} \begin{align*} & l_{r} - share\:of\:the\:employees\:who\:worked\:during\:lockdown \end{align*}
Total costs:
3 trillion 267 billion
3% of the GDP in 2019The most affected regiosn
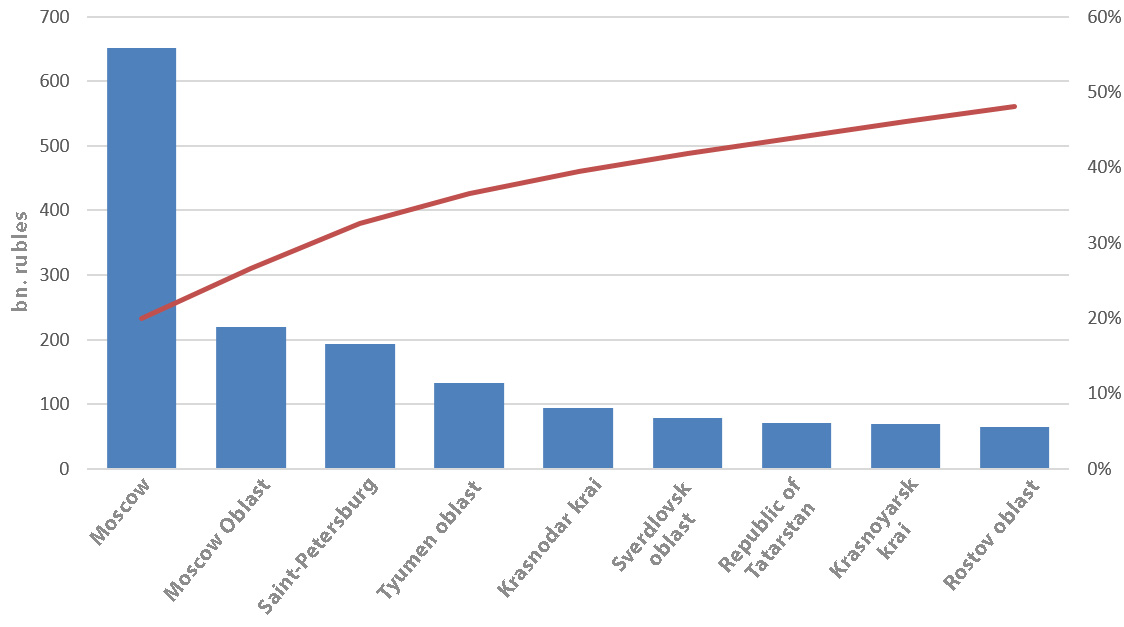
Total costs:
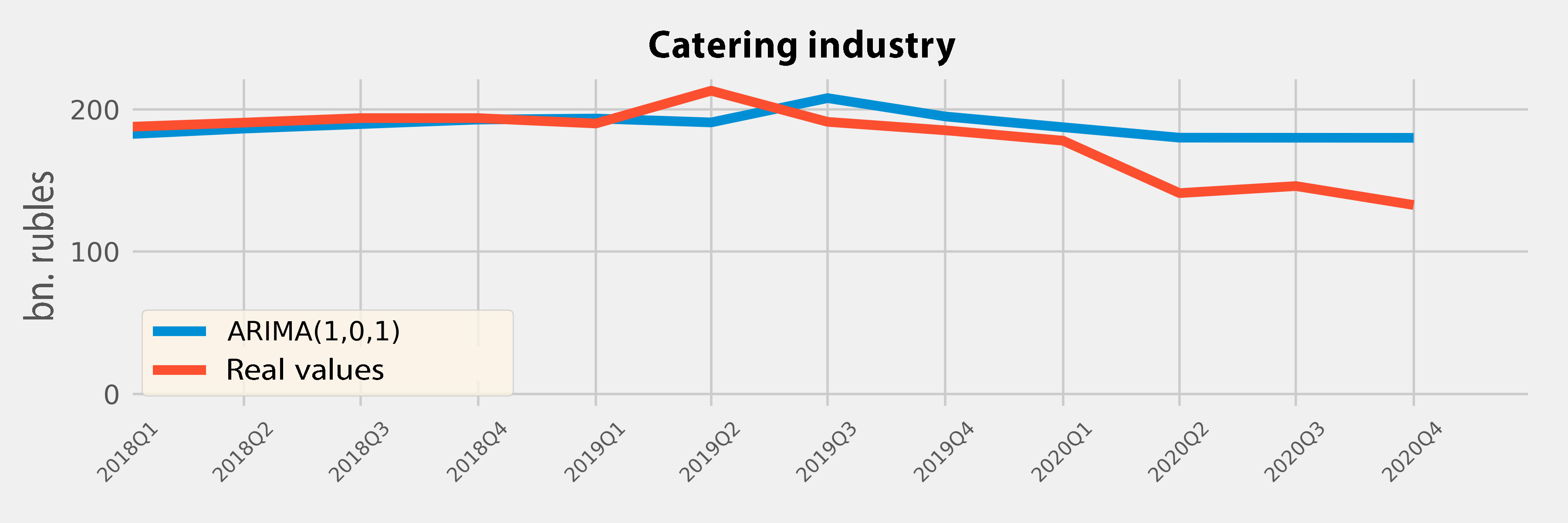
-120.14 billion₽
12% of the GDP in 2019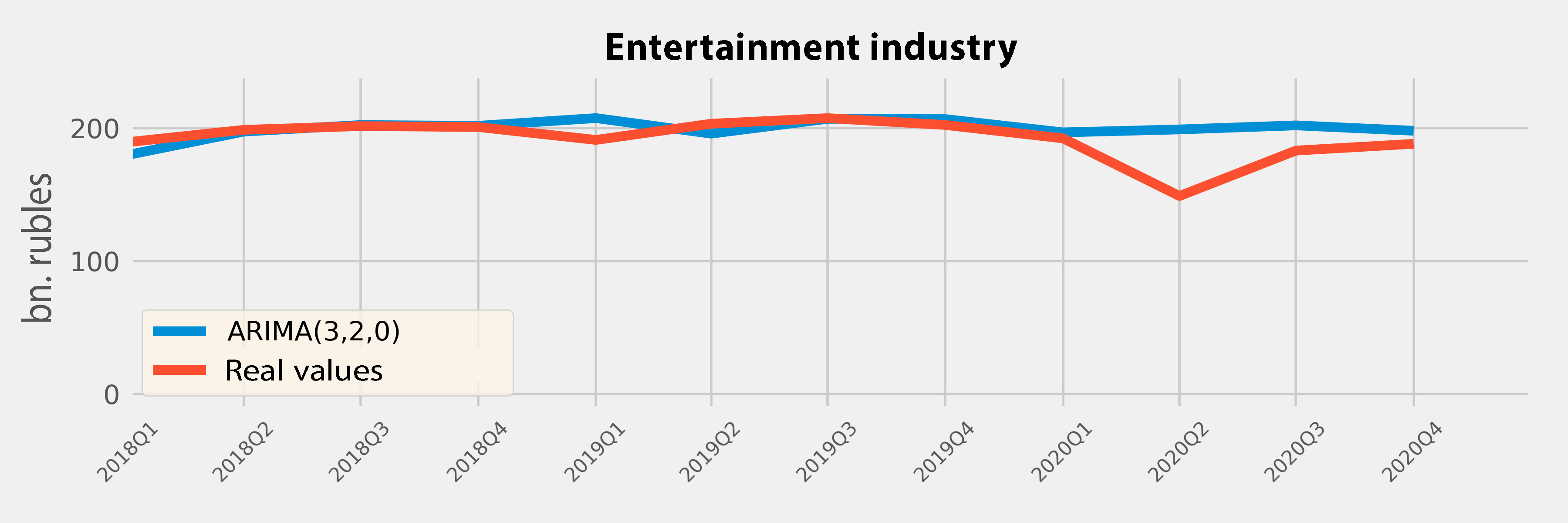
Total costs:
-78.91 billion ₽
9.8% of the GDP in 2019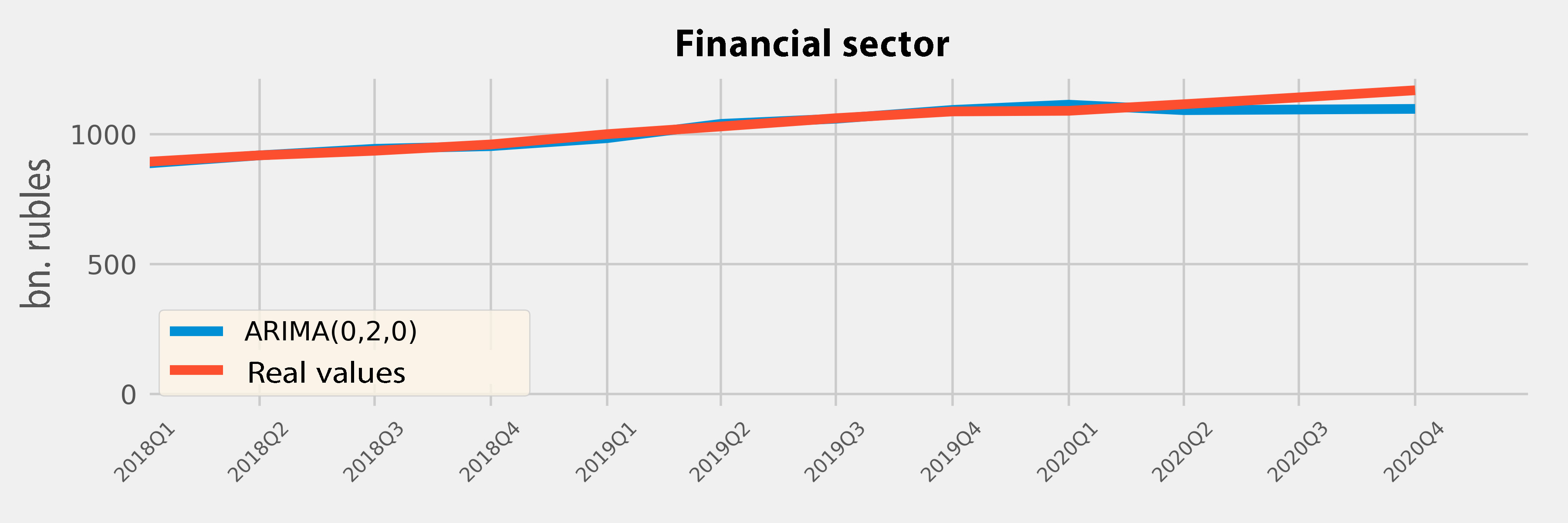
Total income:
141.24 billion ₽
3% of the GDP in 2019Total costs:
-776 billion ₽
6% of the GDP in 2019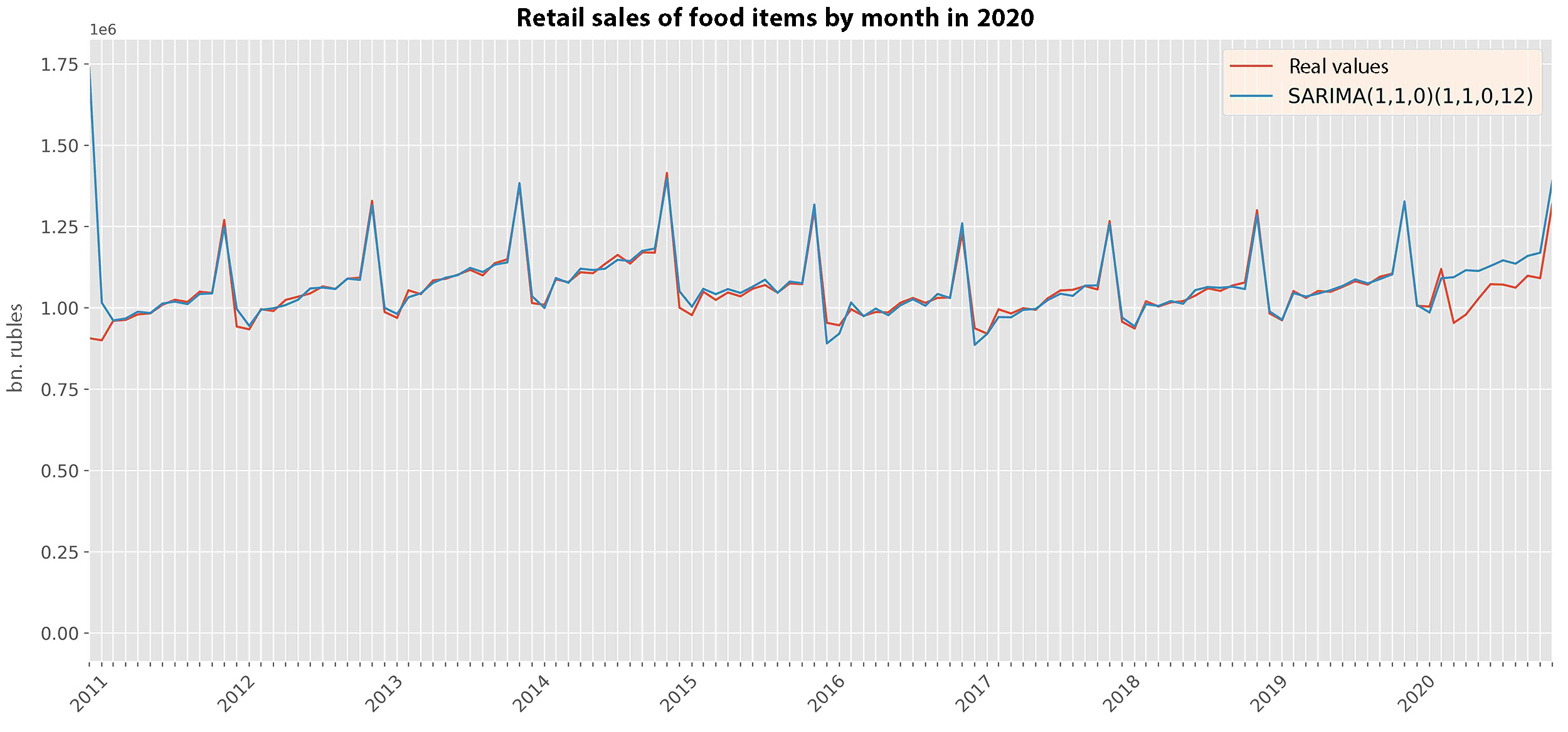
Total costs:
-1 trillion 566 billion ₽
11% of the GDP in 2019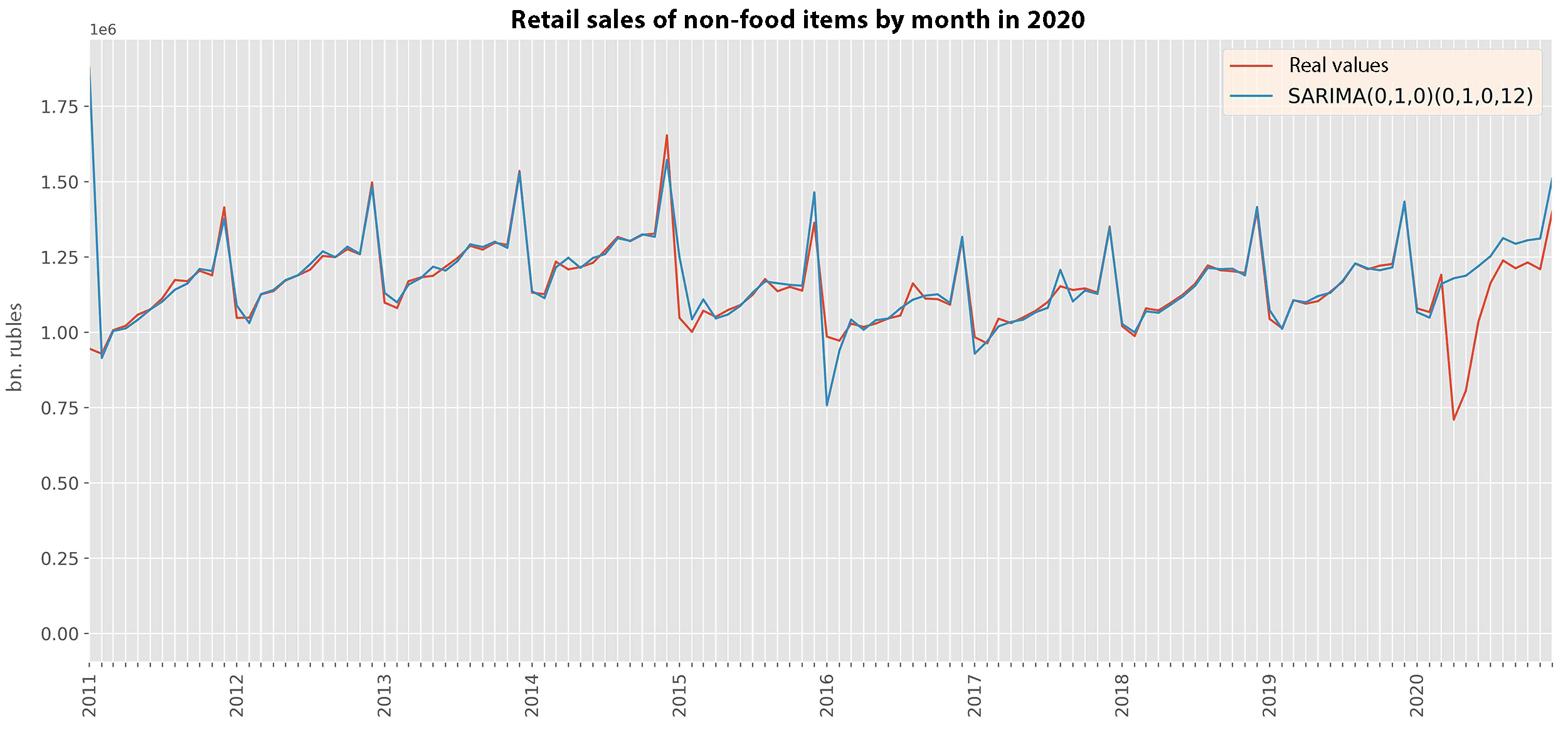
Conclusion
On the whole, the goal of this research has been accomplished. As a result, research of the key methods of assessment and their application to estimate the economic impact of COVID-19 in 2020 have been completed.
Thank you for you attention ! !
Instrumental and mathematical methods to assess the economic impact of COVID-19
Author: Prokofev Savva
Academic advisor: Yurkov Vasiliy, PhD in Mathematics
Reviewer: Meleshkin Mikjail, the CEO of the strategic analysis centre of industrial configuration "Institution of Hypernickel"
Year: 2021